hardness test on mc type carbides in inconel 718|inconel 718 : convenience store Melting Point of Inconel 718. Melting point of Inconel 718 steel is around 1400°C. In general, melting is a phase change of a substance from the solid to the liquid phase. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which this phase change occurs.
Querido John | Netflix. 2010 | Classificação etária: 12 | 1h 47min | Drama. Um soldado em licença se apaixona por uma universitária. Quando ele .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBDigite aqui o nome do curso. A Unopar. Diferenciais da Unopar Nossa História Unidades Documentos Bibliotecas Parcerias e Convênios Registro de Diplomas Registro de Diplomas EAD Ouvidoria Seja um promotor da Educação Editais / Resultados / Regulamentos Portal de Privacidade Seja um parceiro da Unopar Portal de Extensão .
ni based inconel 718
Precipitates in Ni-based superalloys play an important role in improving the mechanical properties such as hardness, strength and creep rupture life.7,8)Inconel 718 can easily form precipitates . The ultimate tensile strength was 828 ± 8 MPa, the true plastic strain at failure 28 ±2%, the micro Vickers hardness 266± 21 HV200, and the dynamically measured Young s .
Inconel 718 (IN718) is a nickel-base superalloy with high static strength and excellent resistance to creep and rupture at elevated temperatures [1].Its superior corrosion and oxidation resistance makes it a desirable container material for molten salt reactors [2] as well as a material for rocket motors and for blades, disks, shafts, and fasteners in industrial gas .
tensile stress testing machine
INCONEL ® alloy 625 Tensile Properties and Hardness Typical tensile properties of annealed and solution-treated material from room to elevated temperature are shown in Figures 3, 4, and 5. The approximate relationship between the hardness and tensile and yield strength of strip is shown in Figure 6. Increased tensile properties for service at Hardness measurements (Figure 15) support these conclusions, showing similar hardness for IN718-TiC and IN718-NbC, and lower hardness for IN718-B 4 C despite higher carbide precipitate fractions. Another significant factor differentiating IN718/IN718-NbC and IN718-TiC/IN718-B 4 C is the grain morphology and crystallographic texture.Melting Point of Inconel 718. Melting point of Inconel 718 steel is around 1400°C. In general, melting is a phase change of a substance from the solid to the liquid phase. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which this phase change occurs. The tests discussed in the article aimed to analyse the structure and hardness of the heat affected zone and that of the weld in thin butt joints (1.0 mm) made of Inconel 718 using the TIG method and variable welding linear energy restricted within the range of 45 J/mm to 80 J/mm. The test joints were subjected to visual tests, macro and microscopic metallographic .
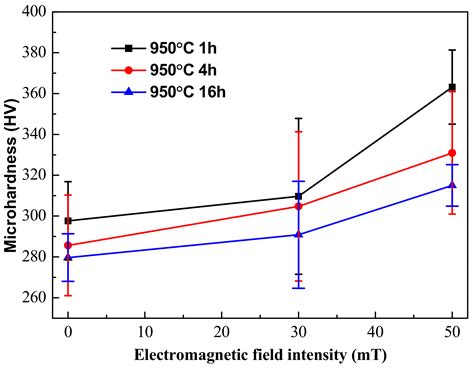
At the same time, many MC-type carbides are not observed in the LSP + HT sample due to the grain produced by LSP refinement and a large number of sub-structures to inhibit the segregation of Nb . IN718 is a nickel-based superalloy widely used in high-temperature applications including turbine engines and power generation because of its excellent mechanical properties (yield strength up to 650–700 °C, impact strength and fracture toughness down to −40 °C) and corrosion resistance.The precipitation phases in the laser clad IN718 alloy coating include .
In this work, an attempt was made to join Inconel 718 by FSW using a tungsten carbide tool. The influence of major operating parameters such as rotational and traverse speed on the thermal history, axial force, mechanical and microstructural properties of welded samples was investigated. To obtain a sound weld joint, lower rotational speed (i.e., 300 rpm) and . This study explores the potential of a microwave hybrid heating (MHH) technique as an efficient post-heat treatment route for an Inconel 718 (IN718) superalloy processed by laser powder bed fusion .
MC-type carbides (Ref 25). Accordingly, the precipitates with substructure have been attributed to the Laves phase, and the other to the MC carbides (Fig. 3). 3.2 Mechanical Testing Figure 5 presents the stress-true strain curves for different strain rates. All the curves exhibit yielding, extensive plasticity It is worth mentioning that, among all carbide types in IN718 alloy, MC carbides form at high temperature, and are distinguished by their high Nb and Ti contents, unlike M 6 C and M 23 C 6 . In the present study, we systematically identify and characterize a (Nb, Mo)-rich M23C6 type of M23C6 carbide with a lattice parameter of 1.094 nm in alloy 718 for the first time using a combination of selected area electron diffraction pattern and powder X-ray diffraction analysis. The time-temperature-precipitation diagrams of the precipitates in both annealed and . At the same time, carbides such as the MC-type carbides [(Nb,Ti)C] formed primarily during solidification play a key part in the mechanical properties of nickel-based superalloy. Generally speaking, the properties of the Inconel 718 are determined by the size and morphology of the γ ', γ '', and δ phases as well as carbides, which can be .
Besides IN718, Hastelloy X (Hast-X) also deserves our close attention especially in terms of high temperature oxidation resistance. Hast-X is a solution strengthening nickel-based superalloy containing high amounts of molybdenum as well as lower percentages of tungsten and cobalt [20].And its resistance to high temperature oxidation (short-term operating temperature . The as-received commercial Inconel 718 material was solid solution heat treated (ST), cold-rolled (CR), and precipitation-hardened (PH) to investigate the effects of deformation on the tensile properties, hardness, and .
A series of Inconel 718 alloys modified by additions of 0.1-0.3 of a mixture of rare earth elements Ce:La:Nd:Pr have been synthesized by powder metallurgy. These alloys were sintered by conventional and hot isostatic pressure methods and subject to standard aging treatment. The results showed that adding rare earth elements generates γ′ and γ″ precipitates .
Inconel 718 alloy is a precipitation-hardening nickel-base superalloy with nominal carbon content below 0.08 wt.%. This carbon is almost insoluble in the Inconel 718 matrix phase and is segregated during solidification [].As a result, primary NbC carbides with a face-centered cubic structure are precipitated in the as-cast condition [2, 3].The strength of Inconel 718 .
strength and creep rupture life.7,8) Inconel 718 can easily form precipitates such as intermetallic compounds (£A and £AA) and metalcarbon (MC) carbides at elevated temperatures.7,8) In particular, the formation of precipitates in the grains and grain boundaries in Inconel 718 alloy has been reported to be The tensile and the micro-hardness mechanical properties were studied for aging at 680 and 750 °C at 4, 50 and 100 h aging duration. . these are primary carbides of the MC type. The study by X-ray . it should be noted that, for a tensile test, the bursting strength of Inconel 718 disks is strongly influenced by the ultimate tensile . The microstructure of Inconel 625 after welding or fusion-based additive manufacturing cannot be directly compared with its wrought counterparts, as the enrichment of Nb in the interdendritic region during solidification favours the formation of MC (M: Nb, Ti) carbides and Laves phase (A 2 B, A: Ni, Cr, and Fe; B: Nb, Mo, Ti; D0 24; hexagonal; P6 3 /mmc) by .Materials. In the present study, Inconel 718 (IN718) superalloy fabricated by laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) has been characterized focusing on the effect of both homogenization and solution treatment time on grains structure, crystallographic texture, precipitates formation/dissolution and material hardness.

The grain sizes in the WZ of joints 1# and 3# were 112.6 µm and 106.7 µm, respectively, which was ascribed to the precipitation of the Laves phases and MC carbides. The current investigation delved into the friction and wear characteristics of abrasive-finished Inconel 718 alloys fabricated by additive manufacturing and casting methods. Silicon carbide balls were used as counter-body materials for all tribology tests. Variable loads of 10 N, 20 N, and 30 N were applied, along with frequencies of 5 Hz and 15 Hz, while . Dissimilar welding joints of Inconel 718 (IN718) nickel superalloy with low-carbon AISI 304L austenitic steel (SS304L) were conducted using the Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding process. The present investigation focuses on the effect of different welding currents on the produced dissimilar joints’ microstructure and mechanical properties. The microstructure study .
A slab of dimension (152 \(\times\) 25 \(\times\) 18) mm 3 is successfully fabricated through Cold Metal Transfer + Metal Inert Gas-based Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM). 4.3 kg/h deposition rate is achieved. WAAMed Inconel 718 exhibits dendritic microstructure which grows along the build direction. In the solid solution matrix of Ni–Cr–Fe, Laves phase, Nb-rich . The influence of post-welding heat treatment (PWHT) on the microstructure, hardness, and corrosion behavior of Inconel 625 weld metal deposited by the Electro Slag Strip Cladding (ESSC) Process was investigated. Microstructural characterization was performed by scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and transmission electron microscopy. Cyclic .
Inconel 718 Plus is a nickel-based heat resistant superalloy (HRSA) material with a machinability rating of 10% and hardness of 42 HRC. Inconel 718 Plus has 53% nickel and additional alloying elements per the table below. . Recommended Carbide Grades for Material Inconel 718 Plus. Turning; Parting Off; Grooving;
lloyd tensile testing machine
bolo com topo de morango para o aniversário de meu marido.
hardness test on mc type carbides in inconel 718|inconel 718